轻松掌握XMLHttpRequest对象
XmlHttp是什么?
最通用的定义为:XmlHttp是一套可以在Javascript、VbScript、Jscript等脚本语言中通过http协议传送或从接收XML及其他数据的一套API。XmlHttp最大的用处是可以更新网页的部分内容而不需要刷新整个页面。
来自MSDN的解释:XmlHttp提供客户端同http服务器通讯的协议。客户端可以通过XmlHttp对象(MSXML2.XMLHTTP.3.0)向http服务器发送请求并使用微软XML文档对象模型Microsoft® XML Document Object Model (DOM)处理回应。 现在的绝对多数浏览器都增加了对XmlHttp的支持,IE中使用ActiveXObject方式创建XmlHttp对象,其他浏览器如:Firefox、Opera等通过window.XMLHttpRequest来创建xmlhttp对象。
XmlHttp对象的属性:

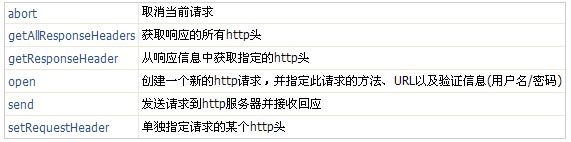
XmlHttp对象的方法:
如何发送一个简单的请求?
最简单的请求是,不以查询参数或提交表单的方式向服务器发送任何信息.使用XmlHttpRequest对象发送请求的基本步骤:
● 为得到XmlHttpRequest对象实例的一个引用,可以创建一个新的XmlHttpRequest的实例。
● 告诉XmlHttpRequest对象,那个函数回处理XmlHttpRequest对象的状态的改变.为此要把对象的
onreadystatechange属性设置为指向JavaScript的指针.
● 指定请求属性.XmlHttpRequest对象的Open()方法会指定将发送的请求.
● 将请求发送给服务器.XmlHttpRequest对象的send()方法将请求发送到目标资源.
XmlHttpRequest实例分析
我想大家都知道,要想使用一不对象首先我门得做什么?是不是必须先创建一个对象吧.比如C#和Java里用new来实例对象.那么我门现在要使用XmlHttp对象是不是也应该先创建一个XmlHttp对象呢?这是毫无疑问的!那么下面我们来看看在客户端怎么创建一个XmlHttp对象,并使用这个对象向服务端发送Http请求,然后处理服务器返回的响应信息.
1.创建一个XmlHttp对象(在这里我以一个无刷新做加法运算的实例 )
var xmlHttp;
function createXMLHttpRequest()
{
if(window.ActiveXObject)
{
xmlHttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
else if(window.XMLHttpRequest)
{
xmlHttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
}
}
2.定义发送请求的方法
//处理方法
function AddNumber()
{
createXMLHttpRequest();
var url= "AddHandler.ashx?num1="+document.getElementById("num1").value+"&num2="+document.getElementById("num2").value;
xmlHttp.open("GET",url,true);
xmlHttp.onreadystatechange=ShowResult;
xmlHttp.send(null);
}
3.定义回调函数,用于处理服务端返回的信息
//回调方法
function ShowResult()
{
if(xmlHttp.readyState==4)
{
if(xmlHttp.status==200)
{
document.getElementById("sum").value=xmlHttp.responseText;
}
}
}
在上面这个实例中,是在客户端想服务端的AddHandler.ashx发送的请求,并传递两个参数(也就是待相加的数)过去,下面我门来看看服务端是怎么处理接收传递过去的两个参数以及怎么实现加法运算并返回结果到客户端的.代码如下:
<%@ WebHandler Language="C#" Class="Handler" %>
using System;
using System.Web;
using System.Data;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
public class Handler : IHttpHandler
{
public void ProcessRequest (HttpContext context)
{
context.Response.ContentType = "text/plain";
int a = Convert.ToInt32(context.Request.QueryString["num1"]);
int b = Convert.ToInt32(context.Request.QueryString["num2"]);
int result = a + b;
context.Response.Write(result);
}
public bool IsReusable
{
get
{
return false;
}
}
}
现在我门就可以调用AddNumber()这个方法向服务端发送请求来做一个无刷新的加法运算了.
<div style="text-align: center">
<br />无刷新求和示例<br />
<br />
<input id="num1" style="width: 107px" type="text" onkeyup="AddNumber();" value="0" />
+<input id="num2" style="width: 95px" type="text" onkeyup="AddNumber();" value="0" />
=<input id="sum" style="width: 97px" type="text" /></div>
运行结果如下:

这个实例虽然很简单.我之所以用这个实例主要是给大家介绍XmlHttp对象的处理过程.文章后面我把项目文件提供下载.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
上面把JS写到页面中了,在实际的项目开发中是不推荐这样做的,最好把JS代码都定义到一个JS文件类.我这里有一份XmlHttpRequest对象的JS(网上下载的),把相关的方法基本都写全了.下面我门来看看怎么使用这个外部JS文件来发送异步请求及响应.
我门先来看看这个JS文件的详细定义:
function CallBackObject()
{
this.XmlHttp = this.GetHttpObject();
}
CallBackObject.prototype.GetHttpObject = function()
{
var xmlhttp;
if (!xmlhttp && typeof XMLHttpRequest != ‘undefined‘) {
try {
xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
} catch (e) {
xmlhttp = false;
}
}
return xmlhttp;
}
CallBackObject.prototype.DoCallBack = function(URL)
{
if( this.XmlHttp )
{
if( this.XmlHttp.readyState == 4 || this.XmlHttp.readyState == 0 )
{
var oThis = this;
this.XmlHttp.open(‘POST‘, URL);
this.XmlHttp.onreadystatechange = function(){ oThis.ReadyStateChange(); };
this.XmlHttp.setRequestHeader(‘Content-Type‘, ‘application/x-www-form-urlencoded‘);
this.XmlHttp.send(null);
}
}
}
CallBackObject.prototype.AbortCallBack = function()
{
if( this.XmlHttp )
this.XmlHttp.abort();
}
CallBackObject.prototype.OnLoading = function()
{
// Loading
}
CallBackObject.prototype.OnLoaded = function()
{
// Loaded
}
CallBackObject.prototype.OnInteractive = function()
{
// Interactive
}
CallBackObject.prototype.OnComplete = function(responseText, responseXml)
{
// Complete
}
CallBackObject.prototype.OnAbort = function()
{
// Abort
}
CallBackObject.prototype.OnError = function(status, statusText)
{
// Error
}
CallBackObject.prototype.ReadyStateChange = function()
{
if( this.XmlHttp.readyState == 1 )
{
this.OnLoading();
}
else if( this.XmlHttp.readyState == 2 )
{
this.OnLoaded();
}
else if( this.XmlHttp.readyState == 3 )
{
this.OnInteractive();
}
else if( this.XmlHttp.readyState == 4 )
{
if( this.XmlHttp.status == 0 )
this.OnAbort();
else if( this.XmlHttp.status == 200 && this.XmlHttp.statusText == "OK" )
this.OnComplete(this.XmlHttp.responseText, this.XmlHttp.responseXML);
else
this.OnError(this.XmlHttp.status, this.XmlHttp.statusText, this.XmlHttp.responseText);
}
}
一个简单的Hello实例:
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" >
<head runat="server">
<title>HelloWorld实例</title>
<script language="jscript" src="CallBackObject.js"></script>
<script language=jscript>
function createRequest()
{
var name = escape(document.getElementById("name").value);
var cbo = new CallBackObject();
cbo.OnComplete = Cbo_Complete;
cbo.onError = Cbo_Error;
cbo.DoCallBack("HelloWorldServer.aspx?name=" + name);
}
function Cbo_Complete(responseText, responseXML)
{
alert(responseText);
}
function Cbo_Error(status, statusText, responseText)
{
alert(responseText);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<form id="form1" runat="server">
<DIV style="DISPLAY: inline; FONT-WEIGHT: bold; FONT-SIZE: 30px; FONT-FAMILY: Arial, Verdana"
ms_positioning="FlowLayout">Hello, Ajax!</DIV>
<HR width="100%" SIZE="1">
<input type="text" id="name">
<br>
<input type="button" value="发送请求" onclick="javascript:createRequest()">
</form>
</body>
</html>
关于XmlHttpRequest对象就介绍到这里,更多更详细的内容请大家查看相关资料.
欢迎拍砖指正,不甚感激!
本文实例源代码下载
郑重声明:本站内容如果来自互联网及其他传播媒体,其版权均属原媒体及文章作者所有。转载目的在于传递更多信息及用于网络分享,并不代表本站赞同其观点和对其真实性负责,也不构成任何其他建议。






































