基于spark1.3.1的spark-sql实战-01
OK !好久不见,大家都忙着各自的事情,me too, 博客也好久木有更新了,因为一直比较忙
spark sql 三个核心部分:
1. 可以加载各种结构化数据源(e.g., JSON, Hive, and Parquet).
2. 可以让你通过SQL ,spark 内部程序或者外部工具,通过标准的数据库连接(JDBC/ODBC)连接spark,比如一个商业智能的工具Tableau
3.当你通过使用spark程序,spark sql 提供丰富又智能的SQL或者 regular Python/Java/Scala code,包括 join RDDS ,SQL tables ,使用SQL自定义用户函数
DataFrames
A DataFrame is a distributed collection of data organized into named columns. It is conceptually equivalent to a table in a relational database or a data frame in R/Python, but with richer optimizations under the hood. DataFrames can be constructed from a wide array of sources such as: structured data files, tables in Hive, external databases, or existing RDDs.
SQLContext:
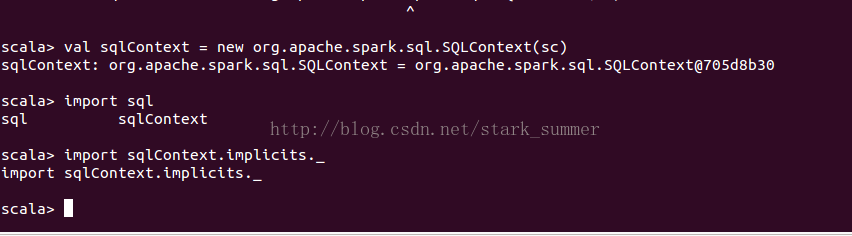
除了SQLContext之外 ,还有HiveContext 来创建,HiveContext包含是SQLContext的,功能比SQLContext更强大,可以操作HiveQL还可以定义UDF,在spark1.3.1以后版本更推荐使用HiveContext,但是需要依赖Hive jar包
Creating DataFrames
拥有SQLContext就可以创建DataFrames from an existing RDD, from a Hive table, or from data sources.
由于Hadoop使用了 lzo压缩方式,所以也需要在spark指定Hadoop Lzo的jar包,否则会报错”Compression codec com.hadoop.compression.lzo.LzoCodec not found.“
在spark_home/conf/spark_env.sh目录增加如下配置:
export SPARK_LIBRARY_PATH=$SPARK_LIBRARY_PATH:/home/wangyue/opt/hadoop/hadoop-2.3.0-cdh5.1.0/lib/native/Linux-amd64-64/*:/home/wangyue/opt/hadoop/hadoop-2.3.0-cdh5.1.0/share/hadoop/common/hadoop-lzo-0.4.15-cdh5.1.0.jar
export SPARK_CLASSPATH=$SPARK_CLASSPATH:/home/wangyue/opt/hadoop/hadoop-2.3.0-cdh5.1.0/share/hadoop/common/hadoop-lzo-0.4.15-cdh5.1.0.jar
重启spark集群后:
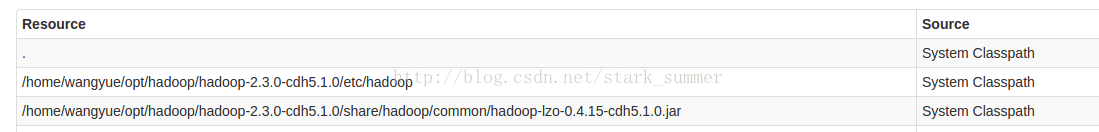
已经可以在classpath中看到lzo jar
加载Json文件:

通过show方法查询dataframe数据

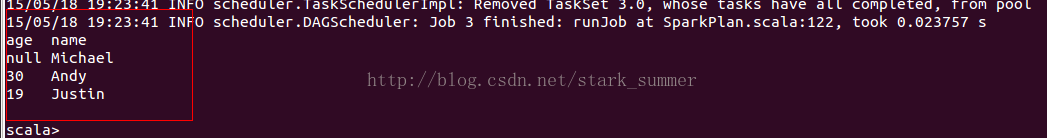
DataFrame Operations



// Select everybody, but increment the age by 1


// Select people older than 21

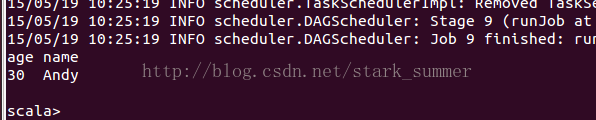
// Count people by age


Running SQL Queries Programmatically
The sql function on a SQLContext enables applications to run SQL queries programmatically and returns the result as a DataFrame.
val sqlContext = ... // An existing SQLContextval df = sqlContext.sql("SELECT * FROM table")
目前1.3.1版本后 可以通过SQLContext 运行 SQL程序,然后返回DataFrame格式的结果
目前有两种方式将RDD 转成DataFrame
1. Inferring the Schema Using Reflection
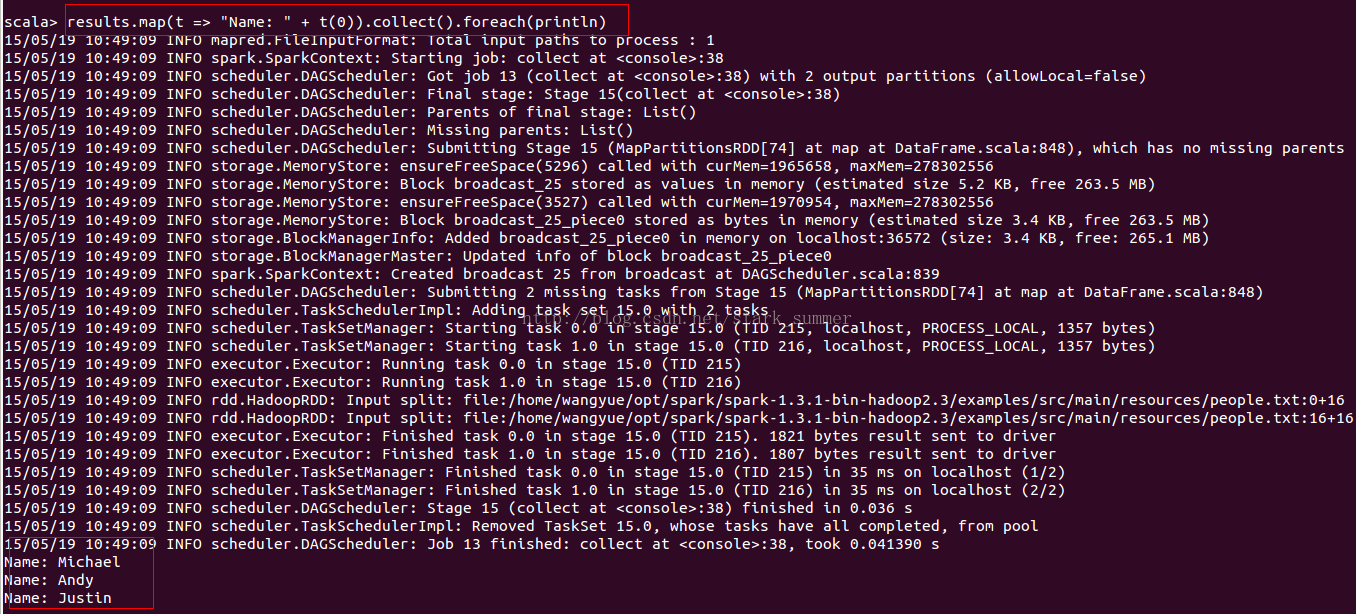
// sc is an existing SparkContext.val sqlContext = new org.apache.spark.sql.SQLContext(sc)// this is used to implicitly convert an RDD to a DataFrame.import sqlContext.implicits._// Define the schema using a case class.// Note: Case classes in Scala 2.10 can support only up to 22 fields. To work around this limit,// you can use custom classes that implement the Product interface.case class Person(name: String, age: Int)// Create an RDD of Person objects and register it as a table.val people = sc.textFile("file:///home/wangyue/opt/spark/spark-1.3.1-bin-hadoop2.3/examples/src/main/resources/people.txt").map(_.split(",")).map(p => Person(p(0), p(1).trim.toInt)).toDF()people.registerTempTable("people")// SQL statements can be run by using the sql methods provided by sqlContext.val teenagers = sqlContext.sql("SELECT name FROM people WHERE age >= 13 AND age <= 19")// The results of SQL queries are DataFrames and support all the normal RDD operations.// The columns of a row in the result can be accessed by ordinal.teenagers.map(t => "Name: " + t(0)).collect().foreach(println)

2. Programmatically Specifying the Schema
When case classes cannot be defined ahead of time (for example, the structure of records is encoded in a string, or a text dataset will be parsed and fields will be projected differently for different users), a DataFrame can be created programmatically with three steps.
Create an RDD of
Rows from the original RDD;Create the schema represented by a
StructTypematching the structure ofRows in the RDD created in Step 1.Apply the schema to the RDD of
Rows viacreateDataFramemethod provided bySQLContext.
For example:
// sc is an existing SparkContext.val sqlContext = new org.apache.spark.sql.SQLContext(sc)// Create an RDDval people = sc.textFile("file:///home/wangyue/opt/spark/spark-1.3.1-bin-hadoop2.3/examples/src/main/resources/people.txt")// The schema is encoded in a stringval schemaString = "name age"// Import Row.import org.apache.spark.sql.Row;// Import Spark SQL data typesimport org.apache.spark.sql.types.{StructType,StructField,StringType};// Generate the schema based on the string of schemaval schema =
StructType(
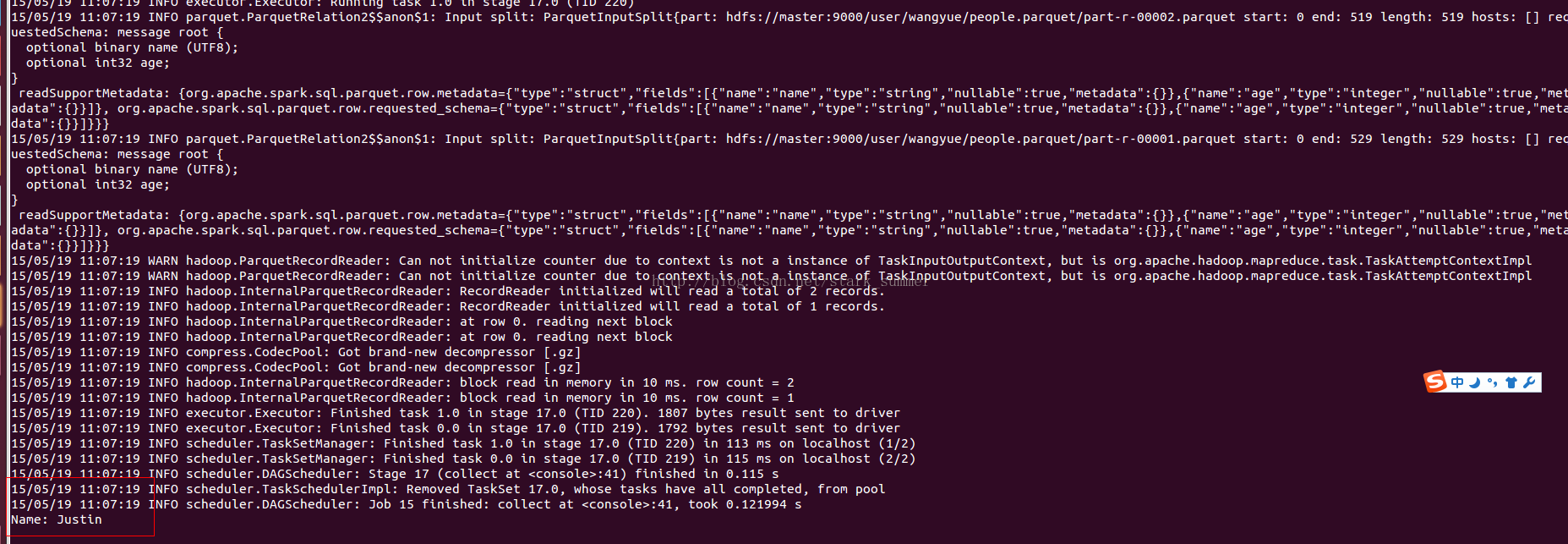
schemaString.split(" ").map(fieldName => StructField(fieldName, StringType, true)))// Convert records of the RDD (people) to Rows.val rowRDD = people.map(_.split(",")).map(p => Row(p(0), p(1).trim))// Apply the schema to the RDD.val peopleDataFrame = sqlContext.createDataFrame(rowRDD, schema)// Register the DataFrames as a table.peopleDataFrame.registerTempTable("people")// SQL statements can be run by using the sql methods provided by sqlContext.val results = sqlContext.sql("SELECT name FROM people")// The results of SQL queries are DataFrames and support all the normal RDD operations.// The columns of a row in the result can be accessed by ordinal.results.map(t => "Name: " + t(0)).collect().foreach(println)
Data Sources
1. Generic Load/Save Functions
yal df = sqlContext.load("people.parquet")df.select("name", "age").save("namesAndAges.parquet")
2. Manually Specifying Options
val df = sqlContext.load("people.json", "json")df.select("name", "age").save("namesAndAges.parquet", "parquet")
Save Modes

Saving to Persistent Tables
在HiveContext 下,DataFrame 会使用saveAsTable命令会将数据等信息保存到HiveMetastore中,这样即使重启启动spark sql还能活取到HiveMetastore中的数据
在SQLContext下,DataFrame 会使用saveAsTable命令会将数据等信息保存到managed table中,但这些数据通过metastore控制,当表执行drop会删除metastore中数据
Parquet Files
1. Loading Data Programmatically
// sqlContext from the previous example is used in this example.// This is used to implicitly convert an RDD to a DataFrame.import sqlContext.implicits._val people = sc.textFile("file:///home/wangyue/opt/spark/spark-1.3.1-bin-hadoop2.3/examples/src/main/resources/people.txt").map(_.split(",")).map(p => Person(p(0), p(1).trim.toInt)).toDF() ... // An RDD of case class objects, from the previous example.// The RDD is implicitly converted to a DataFrame by implicits, allowing it to be stored using Parquet.people.saveAsParquetFile("people.parquet")// Read in the parquet file created above. Parquet files are self-describing so the schema is preserved.// The result of loading a Parquet file is also a DataFrame.val parquetFile = sqlContext.parquetFile("people.parquet")//Parquet files can also be registered as tables and then used in SQL statements.parquetFile.registerTempTable("parquetFile")val teenagers = sqlContext.sql("SELECT name FROM parquetFile WHERE age >= 13 AND age <= 19")
// sqlContext from the previous example is used in this example.// This is used to implicitly convert an RDD to a DataFrame.import sqlContext.implicits._val people = sc.textFile("file:///home/wangyue/opt/spark/spark-1.3.1-bin-hadoop2.3/examples/src/main/resources/people.txt").map(_.split(",")).map(p => Person(p(0), p(1).trim.toInt)).toDF()// The RDD is implicitly converted to a DataFrame by implicits, allowing it to be stored using Parquet.people.saveAsParquetFile("people.parquet")// Read in the parquet file created above. Parquet files are self-describing so the schema is preserved.// The result of loading a Parquet file is also a DataFrame.val parquetFile = sqlContext.parquetFile("people.parquet")//Parquet files can also be registered as tables and then used in SQL statements.parquetFile.registerTempTable("parquetFile")val teenagers = sqlContext.sql("SELECT name FROM parquetFile WHERE age >= 13 AND age <= 19")teenagers.map(t => "Name: " + t(0)).collect().foreach(println)
Schema merging
/ sqlContext from the previous example is used in this example.// This is used to implicitly convert an RDD to a DataFrame.import sqlContext.implicits._// Create a simple DataFrame, stored into a partition directoryval df1 = sc.makeRDD(1 to 5).map(i => (i, i * 2)).toDF("single", "double")df1.saveAsParquetFile("data/test_table/key=1")// Create another DataFrame in a new partition directory,// adding a new column and dropping an existing columnval df2 = sc.makeRDD(6 to 10).map(i => (i, i * 3)).toDF("single", "triple")df2.saveAsParquetFile("data/test_table/key=2")// Read the partitioned tableval df3 = sqlContext.parquetFile("data/test_table")df3.printSchema()// The final schema consists of all 3 columns in the Parquet files together// with the partiioning column appeared in the partition directory paths.// root// |-- single: int (nullable = true)// |-- double: int (nullable = true)// |-- triple: int (nullable = true)// |-- key : int (nullable = true)

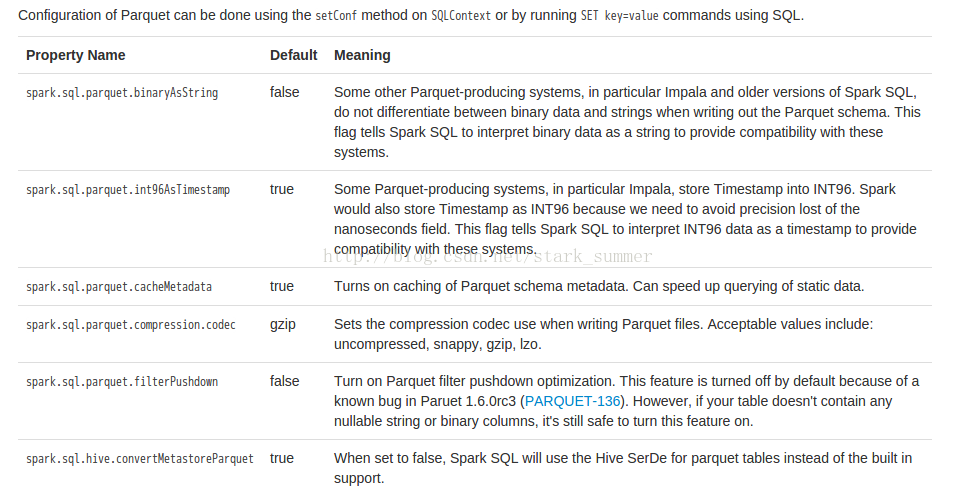
Configuration
JSON Datasets
Spark SQL can automatically infer the schema of a JSON dataset and load it as a DataFrame. This conversion can be done using one of two methods in a SQLContext:
jsonFile- loads data from a directory of JSON files where each line of the files is a JSON object.jsonRDD- loads data from an existing RDD where each element of the RDD is a string containing a JSON object.
Note that the file that is offered as jsonFile is not a typical JSON file. Each line must contain a separate, self-contained valid JSON object. As a consequence, a regular multi-line JSON file will most often fail.
// sc is an existing SparkContext.val sqlContext = new org.apache.spark.sql.SQLContext(sc)// A JSON dataset is pointed to by path.// The path can be either a single text file or a directory storing text files.val path = "file:///home/wangyue/opt/spark/spark-1.3.1-bin-hadoop2.3/examples/src/main/resources/people.json"// Create a DataFrame from the file(s) pointed to by pathval people = sqlContext.jsonFile(path)// The inferred schema can be visualized using the printSchema() method.people.printSchema()// root// |-- age: integer (nullable = true)// |-- name: string (nullable = true)// Register this DataFrame as a table.people.registerTempTable("people")// SQL statements can be run by using the sql methods provided by sqlContext.val teenagers = sqlContext.sql("SELECT name FROM people WHERE age >= 13 AND age <= 19")// Alternatively, a DataFrame can be created for a JSON dataset represented by// an RDD[String] storing one JSON object per string.val anotherPeopleRDD = sc.parallelize( """{"name":"Yin","address":{"city":"Columbus","state":"Ohio"}}""" :: Nil)val anotherPeople = sqlContext.jsonRDD(anotherPeopleRDD)


全部查询:
scala> val anotherPeopleSql = sqlContext.sql("select name,address.city from anotherPeople")
scala> anotherPeopleSql.map(t => "Name: " + t(0)+ " city:"+t(1)).collect().foreach(println)

郑重声明:本站内容如果来自互联网及其他传播媒体,其版权均属原媒体及文章作者所有。转载目的在于传递更多信息及用于网络分享,并不代表本站赞同其观点和对其真实性负责,也不构成任何其他建议。





































