Linux中iptables的一些解读
首先要注意的是iptables不是防火墙,而是实现防火墙功能的工具。
1.iptables的两张框架图:
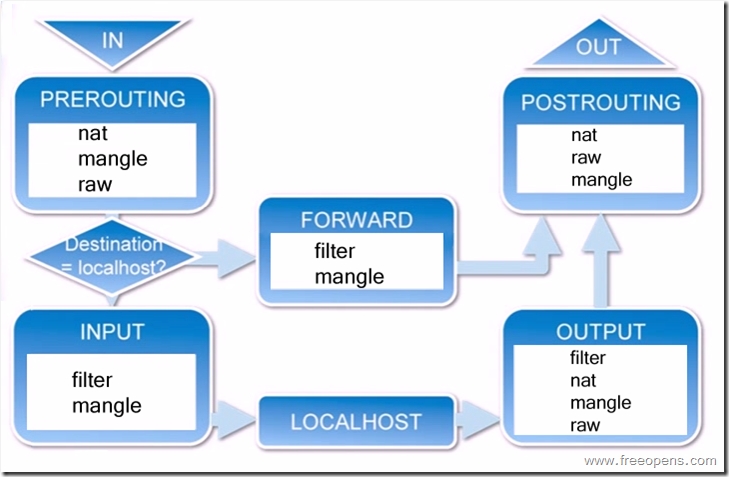
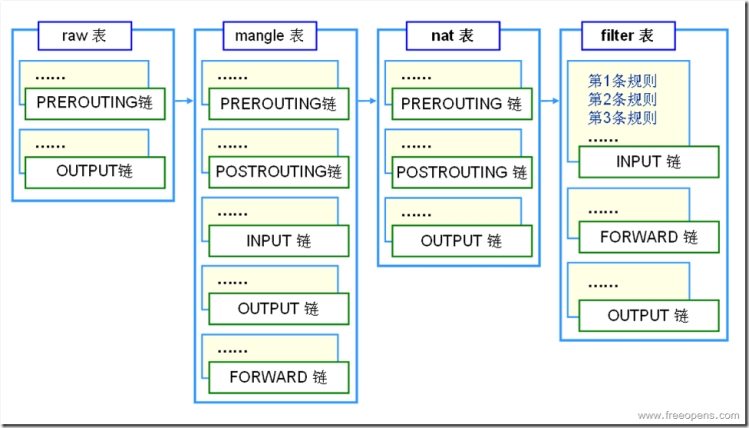
表:
raw表: 对报文设置一个标志,决定数据包是否被状态跟踪机制处理
mangle表: 主要用于修改数据包
nat表: 主要用处是网络地址转换、端口映射
fileter表: 主要用于过滤包
一般情况我们对filter表做配置的更多。
链:
INPUT: 作用于进入本机的包
OUTPUT: 作用于本机送出的包
FORWARD: 匹配穿过本机的数据包(转发)
PREROUTING: 用于修改目的地址(DNAT)
POSTROUTING:用于修改源地址 (SNAT)
2.iptables的基本操作
启动指令:service iptables start 重启指令:service iptables restart 关闭指令:service iptables stop 保存指令:service iptables save 清除规则:iptables -F 将链的记数的流量清零: iptables -Z 清除链: iptables -X 清空iptables时一般-F -Z -X一起使用
iptables -nvL 显示当前已经设置好的防火墙规则 显示结果: [root@wangwq ~]# iptables -nvL Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination 37 4317 ACCEPT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state RELATED,ESTABLISHED 0 0 ACCEPT icmp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 0 0 ACCEPT all -- lo * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 1 52 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state NEW tcp dpt:22 39 4106 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-host-prohibited Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination 0 0 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-host-prohibited Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 37 packets, 5314 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
iptables的三种状态:
ACCEPT 允许
DROP 丢弃
REJECT 拒绝
DROP和REJECT的区别:DROP是直接不让进入,而REJECT是先让进入然后再拒绝,DROP更安全,所以一般拒绝都用DROP。
iptables默认的规则是允许,即
iptables -P INPUT ACCEPT iptables -P OUTPUT ACCEPT iptables -P FORWARD ACCEPT
3.iptables的配置:
iptables的两种配置思路:
1)默认允许,拒绝特别;
2)默认拒绝,允许特别;
二者都有自己的特点,看情况而定。但是注意:如果要选择第二种配置思路,配置前切记先把ssh设置为ACCEPT,因为一般机器不在我们身边,一旦配置默认拒绝,那我们的远程登录就会断开连接,那问题就大了。
配置默认拒绝前设置:
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT
iptables -A OUTPUT -p tcp --sport 22 -j ACCEPT
还有一种方法:做一个计划任务,让iptables定期停止,即执行service iptables stop,这样的话即使配置默认拒绝前没有允许ssh也没关系,等到计划任务生效的时间iptables就会自动清除所有的配置,包括默认规则。
iptables的基本语法:
iptables [-t filter/nat] [-A/I] [INPUT/OUTPUT/FORWARD] [-i/o interface] [-p tcp/udp/icmp/all] [-s ip/network] [--sport ports] [-d ip/network] [--dport ports] [-j ACCEPT/DROP]
不加-t时默认是filter
语法参数:
-I:第一行插入
-A:最后追加
-i/o:指的是数据要进入或出去所要经过的端口,如eth1,eth0,pppoe等
-p:你所要指定的协议
-s:指定来源ip,可是单个ip如192.168.109.131,也可以是一个网络 192.168.109.0/24,还可以是一 个域名如163.com,如果你填写的是域名系统会自动解析出他的ip并在iptables里显示
--sport:来源端口
-d:指定目标端口
--dport:目标端口
-j:执行参数ACCEPT或DROP,REJECT一般不用
如果配置的是INPUT(进入),则来源ip是运程ip,目标端口就是本机;OUTPUT相反,相信可以理解。
4.iptables的执行优先级:
iptables的执行顺序是自上而下,当有配置产生冲突时,前面执行的生效。
5.删除iptables
有时我们需要删除其中一条或几条iptables,那就不能iptables -F 了,删除某一条iptables常用的有两种方法:
1.修改配置文件
# vim /etc/sysconfig/iptables
删除相应的行,然后service iptables restart,再service iptables save.
注意:
修改完配置文件不能先save,一定要先restart才能save,要不然就白做了。因为save会在iptables服务启动时重新加载,要是在重启之前直接先调用了service iptables save 那么你 的/etc/sysconfig/iptables 配置就回滚到上次启动服务的配置了。
2.命令删除
1)如果你记得配置时的写法,那么可以直接iptables -D 后跟上配置时的写法。如:
iptables -D INPUT -s 10.72.11.12 -p tcp --sport 1234 -d 10.72.137.159 --dport 80 -j DROP
2)一般的方法:
a. 查看每条iptables的序号:# iptables -nvL --line-number Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination 1 263 21025 ACCEPT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state RELATED,ESTABLISHED 2 0 0 ACCEPT icmp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 3 0 0 ACCEPT all -- lo * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
b. 根据查看的序号删除:# iptables -D INPUT 2
注意:
1、若规则列表中有多条相同的规则时,按内容匹配只删除序号最小的一条;
2、按号码匹配删除时,确保规则号码小于等于已有规则数,否则报错;
3、按内容匹配删除时,确保规则存在,否则报错。
技术链接: http://www.aminglinux.com/bbs/forum.php
本文出自 “我不是我” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://wangwq.blog.51cto.com/8711737/1634806
郑重声明:本站内容如果来自互联网及其他传播媒体,其版权均属原媒体及文章作者所有。转载目的在于传递更多信息及用于网络分享,并不代表本站赞同其观点和对其真实性负责,也不构成任何其他建议。






































