2015/04/08 Shell基础-1
ps: 红字字体为重要部分, 仔细看
一、shell特性
1. history查看命令历史记录,默认记录1000条;
[root@Shell ~]# history 1 vim /etc/hosts 2 ifconfig 3 cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg- 4 cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 5 ifconfig eth0 up ……………………/省略 [root@Shell ~]# vim /etc/profile #可自定义history历史命令记录;
2. !!执行上条命令;
[root@Shell ~]# !! 1 vim /etc/hosts 2 ifconfig 3 cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg- 4 cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 5 ifconfig eth0 up ……………………/省略
3. !$表示上条命令最后一个参数;
[root@Shell ~]# ls 1.txt 1.txt [root@Shell ~]# ls !$ ls 1.txt 1.txt
4. alias别名;
[root@Shell ~]# alias a="ls" #创建别名; [root@Shell ~]# a 1.tar 1.txt 2.txt anaconda-ks.cfg install.log install.log.syslog [root@Shell ~]# unalias a #取消别名; [root@Shell ~]# a -bash: a: command not found
5. shell中的字符;
*: 表示可以匹配零个或多个字符;
?: 可以匹配一个任意字符;
#: 表示注释;
$: 用来标记一个变量;
~: 表示家目录;
&: 把一条可执行命令放入后台执行;
[]: 表示里面的括号选一个;
6. 重定向(输出)、追加、输入、错误重定向、错误追加;
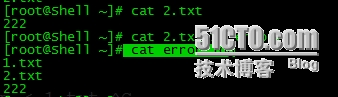
[root@Shell ~]# ls [123].txt > error.log
[root@Shell ~]# cat 2.txt >> error.log
[root@Shell ~]# cat < 2.txt
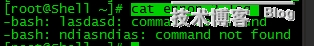
[root@Shell ~]# lasdasd 2> error_2.log
[root@Shell ~]# ndiasndias 2>> error_2.log
7. 作业控制;
[root@Shell ~]# sleep 100 #按Crtl+z放到后台执行; [root@Shell ~]# sleep 200 #按Crtl+z放到后台执行; [root@Shell ~]# sleep 300 #按Crtl+z放到后台执行; [root@Shell ~]# jobs #查看后台执行作业;
[root@Shell ~]# fg 1 #将作业调回到前台执行;
二、变量
1. 自定义变量;
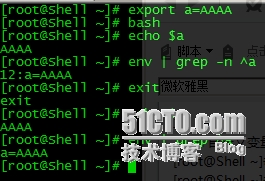
[root@Shell ~]# a=c [root@Shell ~]# set | grep -n ^a #set可以把所有变量列出来; 55:a=c [root@Shell ~]# env | grep ^a #env可以列出的当前用户的所有环境变量; [root@Shell ~]# export a=AAAA #export引入全局变量; [root@Shell ~]# bash [root@Shell ~]# echo $a AAAA [root@Shell ~]# env | grep -n ^a 12:a=AAAA [root@Shell ~]# exit exit [root@Shell ~]# echo $a AAAA
[root@Shell ~]# bash #取消一个自定义变量; [root@Shell ~]# unset a [root@Shell ~]# env | grep ^a
2. 自定义变量中间如果带有空格, 需用引号;
[root@Shell ~]# a=aming Linux -bash: Linux: command not found [root@Shell ~]# a=‘aming Linux‘ [root@Shell ~]# echo $a aming Linux [root@Shell ~]# b=`echo $a` #` `引用里面的值赋值给b; [root@Shell ~]# echo $b aming Linux [root@Shell ~]# b=‘echo $a‘ #‘ ‘只打印出里面的参数; [root@Shell ~]# echo $b echo $a [root@Shell ~]# b="echo $a" #" "引用里面的值并打印; [root@Shell ~]# echo $b echo aming Linux
3. 合并变量;
[root@Shell ~]# a=2 [root@Shell ~]# b=1 [root@Shell ~]# c=$a‘$b‘ [root@Shell ~]# echo $c 2$b [root@Shell ~]# c=$a"$b" [root@Shell ~]# echo $c 21 [root@Shell ~]# c=$a`$b` -bash: 1: command not found
4. 系统变量和用户变量;
[root@Shell ~]# cat /etc/profile [root@Shell ~]# cat /etc/bashrc [root@Shell ~]# cat .bash_profile [root@Shell ~]# cat .bashrc [root@Shell ~]# echo ‘echo "bashrc"‘ >> .bashrc [root@Shell ~]# echo ‘echo "profile"‘ >> .bash_profile [root@Shell ~]# bash bashrc [root@Shell ~]# su - bashrc profile
总结:
/etc/profile和/etc/bashrc属于全局配置.
$HOME/bashrc和$HOME/bash_profile属于用户配置.
一组对所有用户生效, 一组对当前用户生效.
三、Shell常用命令
1. cut分割
-d: 指定分隔符;
-f: 打印第几段;
-c: 指定截取字符;
以‘:‘为分隔符, 打印/etc/passwd第一段到三段的字符; [root@Shell ~]# cut -d ‘:‘ -f 1-3 /etc/passwd | head -3 root:x:0 bin:x:1 daemon:x:2 截取/etc/passwd的第一个字符到第五个字符; [root@Shell ~]# cut -c 1-5 /etc/passwd | head -3 root: bin:x daemo
2. sort排序
-t: 指定分隔符;
-k: 对第几列排序;
-n: 以数字排序(默认从小到大);
-r: 反向排序,结合-n使用;
-u: 去掉重复行;
以‘:‘为分隔符, 以从小到大数字排序/etc/passwd的第三段字符; [root@Shell ~]# sort -t ‘:‘ -k3 -n /etc/passwd root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin ……………………/省略 以‘:‘为分隔符, 以从大到小数字排序/etc/passwd的第三段字符; [root@Shell ~]# sort -t ‘:‘ -k 3 -nr /etc/passwd user1:x:500:500::/home/user1:/bin/bash saslauth:x:499:76:"Saslauthd user":/var/empty/saslauth:/sbin/nologin dhcpd:x:177:177:DHCP server:/:/sbin/nologin nobody:x:99:99:Nobody:/:/sbin/nologin postfix:x:89:89::/var/spool/postfix:/sbin/nologin
3. uniq去重行
-c: 去重行;
[root@Shell ~]# cat 2.txt 222 222 333 222 333 111 222 [root@Shell ~]# uniq -c 2.txt 2 222 1 333 1 222 1 333 1 111 1 222
4. wc统计行数、字符数、词数
-l: 统计行数;
-m: 统计字符数;
-w: 统计词数;
[root@Shell ~]# wc 2.txt 7 7 28 2.txt [root@Shell ~]# wc -l 2.txt 7 2.txt [root@Shell ~]# wc -m 2.txt 28 2.txt [root@Shell ~]# wc -w 2.txt 7 2.txt
5. tr替换字符
[root@Shell ~]# ls | tr ‘1-9‘ ‘A-Z‘ #将数字1-9替换为A-Z;
6. split切割文件
-b: 按文件大小分割;
-l : 按行数分割;
[root@Shell ~]# du -sh 1.txt 160K 1.txt [root@Shell ~]# split -l 20 1.txt
[root@Shell ~]# ls x* | xargs -i mv {} {}.txt #将x*改为x*.txt
[root@Shell ~]# split -l 20 1.txt log #自定义分割完后的名字;7. &&、||、;;
&&: 前面命令执行成功后执行后面命令;
[root@Shell ~]# ls 1.txt && cd /root 1.txt [root@Shell ~]# ls aaaa.txt && cd /home ls: cannot access aaaa.txt: No such file or directory ||: 前面命令执行不成功执行后面; [root@Shell home]# ls aaaa.txt || cd /root/ ls: cannot access aaaa.txt: No such file or directory ;: 前面命令是否执行完成都会执行后面命令; [root@Shell ~]# ss ; cd /tmp
本文出自 “陈小贱。” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://chenxiaojian.blog.51cto.com/9345444/1630205
郑重声明:本站内容如果来自互联网及其他传播媒体,其版权均属原媒体及文章作者所有。转载目的在于传递更多信息及用于网络分享,并不代表本站赞同其观点和对其真实性负责,也不构成任何其他建议。