linux下的CPU、内存、IO、网络的压力测试
一、对CPU进行简单测试:
1、通过bc命令计算特别函数
例:计算圆周率
echo "scale=5000; 4*a(1)" | bc -l -q
MATH LIBRARY
If bc is invoked with the -l option, a math library is preloaded and the default scale is set to 20.
The math functions will calculate their results to the scale set at the time of their call. The math
library defines the following functions:
s (x) The sine of x, x is in radians. 正玄函数
c (x) The cosine of x, x is in radians. 余玄函数
a (x) The arctangent of x, arctangent returns radians. 反正切函数
l (x) The natural logarithm of x. log函数(以2为底)
e (x) The exponential function of raising e to the value x. e的指数函数
j (n,x) The bessel function of integer order n of x. 贝塞尔函数
2、工具二:Super Pi for linux
Super PI是利用CPU的浮点运算能力来计算出π(圆周率),所以目前普遍被超频玩家用做测试系统稳定性和测试CPU计算完后特定位数圆周率所需的时间。
http://www.super-computing.org/
下载页:ftp://pi.super-computing.org/
wget ftp://pi.super-computing.org/Linux/super_pi.tar.gz
tar -xzvf super_pi.tar.gz
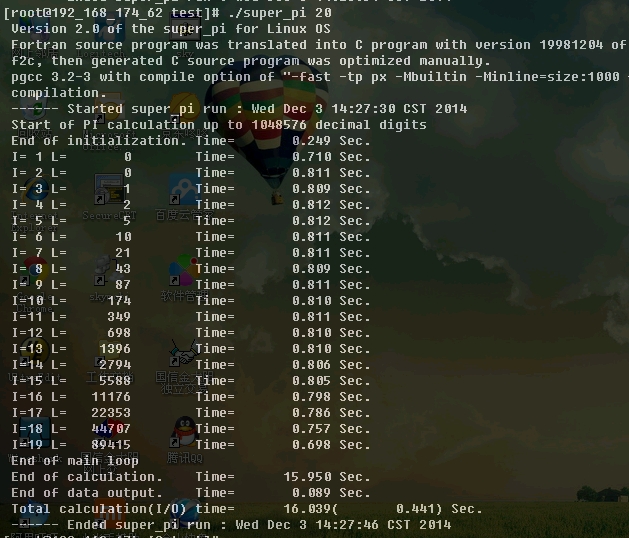
./super_pi 20
20为位数。表示要算2的多少次方位,如通常要算小数点后1M位。
二、对内存进行简单测试:
工具:memtester
官方:http://pyropus.ca/software/memtester/
wget http://pyropus.ca/software/memtester/old-versions/memtester-4.3.0.tar.gz
tar -xzvf memtester-4.3.0.tar.gz
cd memtester-4.3.0
make && make install
用法:Usage: ./memtester [-p physaddrbase [-d device]] <mem>[B|K|M|G] [loops]
例:memtester 1G 5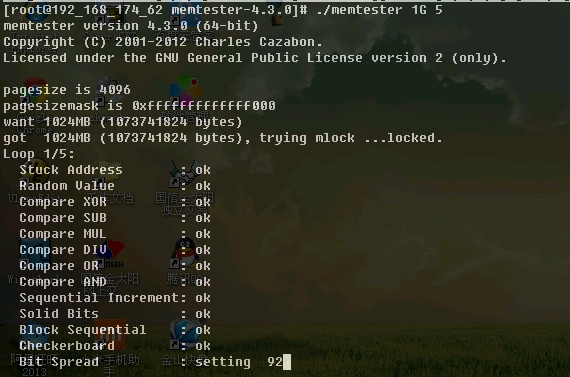
三、对IO进行简单测试:
1、利用dd来进行测试:
time dd if=/dev/zero of=test bs=1M count=4096
用top和iostat查看wa%及写硬盘速度
2、使用fio命令进行测试:
FIO是测试IOPS的非常好的工具,用来对硬件进行压力测试和验证,支持13种不同的I/O引擎,
包括:sync,mmap, libaio, posixaio, SG v3, splice, null, network, syslet, guasi, solarisaio 等等。
说明:
filename=/dev/sdb1 测试文件名称,通常选择需要测试的盘的data目录。
direct=1 测试过程绕过机器自带的buffer。使测试结果更真实。
rw=randwrite 测试随机写的I/O
rw=randrw 测试随机写和读的I/O
bs=16k 单次io的块文件大小为16k
bsrange=512-2048 同上,提定数据块的大小范围
size=5g 本次的测试文件大小为5g,以每次4k的io进行测试。
numjobs=30 本次的测试线程为30.
runtime=1000 测试时间为1000秒,如果不写则一直将5g文件分4k每次写完为止。
ioengine=psync io引擎使用pync方式
rwmixwrite=30 在混合读写的模式下,写占30%
group_reporting 关于显示结果的,汇总每个进程的信息。
此外
lockmem=1g 只使用1g内存进行测试。
zero_buffers 用0初始化系统buffer。
nrfiles=8 每个进程生成文件的数量。
随机读:
fio --filename=/dev/sdb1 --direct=1 --iodepth 1 --thread --rw=randread --ioengine=psync --bs=16k --size=200G --numjobs=10 --runtime=1000 --group_reporting --name=mytest
顺序读:
fio --filename=/dev/sdb1 --direct=1 --iodepth 1 --thread --rw=read --ioengine=psync --bs=16k --size=200G --numjobs=30 --runtime=1000 --group_reporting --name=mytest
随机写:
fio --filename=/dev/sdb1 --direct=1 --iodepth 1 --thread --rw=randwrite --ioengine=psync --bs=16k --size=200G --numjobs=30 --runtime=1000 --group_reporting --name=mytest
顺序写:
fio --filename=/dev/sdb1 --direct=1 --iodepth 1 --thread --rw=write --ioengine=psync --bs=16k --size=200G --numjobs=30 --runtime=1000 --group_reporting --name=mytest
混合随机读写:
fio --filename=/dev/sdb1 --direct=1 --iodepth 1 --thread --rw=randrw --rwmixread=70 --ioengine=psync --bs=16k --size=200G --numjobs=30 --runtime=100 --group_reporting --name=mytest --ioscheduler=noop
本文出自 “秋天的童话” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://wushank.blog.51cto.com/3489095/1585927
郑重声明:本站内容如果来自互联网及其他传播媒体,其版权均属原媒体及文章作者所有。转载目的在于传递更多信息及用于网络分享,并不代表本站赞同其观点和对其真实性负责,也不构成任何其他建议。






































