Android 数据存储(二) 文件的使用
在Android中,我们可以将一些数据直接以文件的形式保存在设备中。例如:一些文本文件、PDF文件、音视频文件和图片等。Android 提供了文件读写的方法。
通过 Context.openFileInput()方法获得标准Java文件输入流(FileInputStream),通过Context.openFileOutput()方法获得标准Java文件输出流( FileOutputStream )。使用
Resources.openRawResource(R.raw.myDataFile)方法返回InputStream。
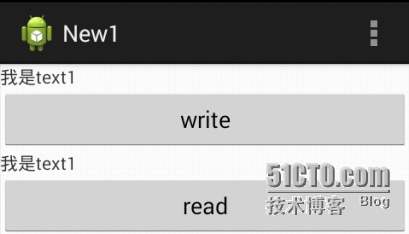
示例如下,新建一个Activity,添加两个TextView和两个Button,点击第一个Button,将TextView上的数据写到文件中,点击第二个Button,将文件中的数据写到TextView中。
MainActivity.java:
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private String filename = "file.txt";
private TextView mytext1,mytext2;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mytext1=(TextView)this.findViewById(R.id.text1);
mytext2=(TextView)this.findViewById(R.id.text2);
Button button1=(Button)this.findViewById(R.id.btn_read);
Button button2=(Button)this.findViewById(R.id.btn_write);
button1.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
mytext2.setText(read());
}
});
button2.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
write(mytext1.getText().toString());
}
});
}
protected String read(){
try {
FileInputStream fis = openFileInput(filename);
try {
byte[] buffer = new byte[fis.available()];
fis.read(buffer);
return new String(buffer);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
protected void write(String str) {
try {
FileOutputStream fos = openFileOutput(filename,MODE_APPEND);
try {
fos.write(str.getBytes());
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}activity_main.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:orientation="vertical"> <TextView android:id="@+id/text1" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="我是text1"/> <Button android:id="@+id/btn_write" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="write"/> <TextView android:id="@+id/text2" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="我是text2"/> <Button android:id="@+id/btn_read" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="read"/> </LinearLayout>
运行结果如下: 点击write将第一个TextView写入文件,点击read将数据读出到第二个TextView

本文出自 “无用大叔” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://aslonely.blog.51cto.com/6552465/1618819
郑重声明:本站内容如果来自互联网及其他传播媒体,其版权均属原媒体及文章作者所有。转载目的在于传递更多信息及用于网络分享,并不代表本站赞同其观点和对其真实性负责,也不构成任何其他建议。



































