定制微型Linux系统
前言
1、使用以下命令获取本机硬件信息:
# cat /proc/cpuinfo # cat /proc/meminfo # lspci -v
2、实验目的
这次实验的目的是:借助于宿主机(正常安装CentOS6.5系统),在目标机上构建一个微型Linux系统,能提供基本的bash命令行接口,提供基本的网络功能,提供用户登录接口和完成身份验证,提供远程连接功能,提供nginx功能。
3、实验说明
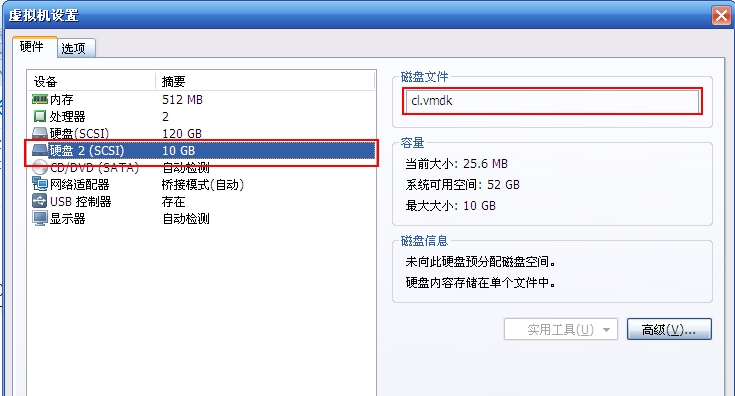
(1)宿主机:正常安装CentOS6.5系统(ip : 192.168.1.152)
把宿主机上的第二块磁盘cl.vmdk作为目标机上仅有的一块磁盘。
(2)目标机
使用VMware创建目标机时,不创建新的磁盘,而是使用宿主机上的第二块磁盘作为目标机的唯一一块磁盘。
注意:目标机只有一块磁盘。
一、提供一个基本的bash命令行接口
注意:记得在宿主机上进行的操作,一定要使用sync命令同步到对应磁盘上。
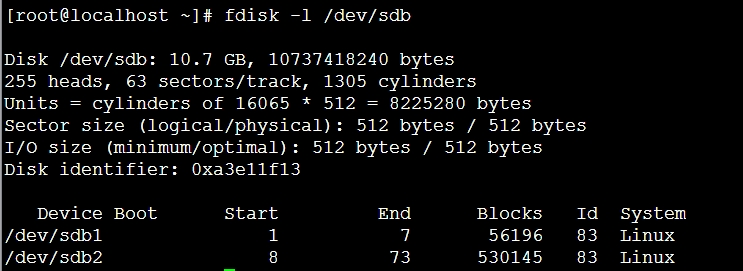
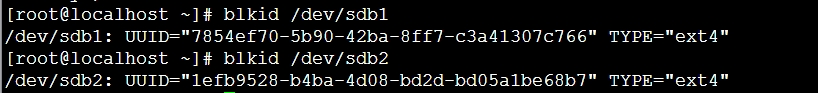
1、在宿主机的另一块磁盘/dev/sdb 上分区、格式化、挂载
(1)分区
/dev/sdb1 50M
/dev/sdb2 512M
(2)格式化
# mke2fs -t ext4 /dev/sdb1 # mke2fs -t ext4 /dev/sdb2
(3)挂载
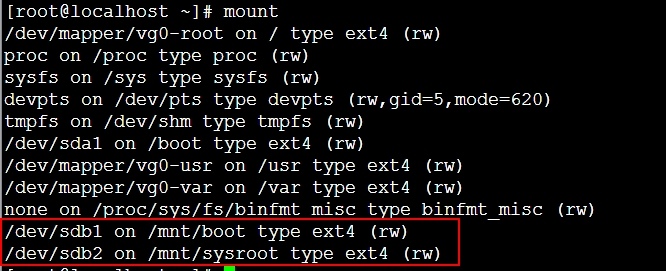
# mkdir -pv /mnt/{boot,sysroot}
# mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt/boot
# mount /dev/sdb2 /mnt/sysroot2、编译内核
下载Linux内核源代码linux-3.13.6.tar.xz 并解压到/usr/src中
# tar xf linux-3.13.6.tar.xz -C /usr/src
创建软链接
# cd /usr/src # ln -sv linux-3.13.6 linux `linux‘ -> `linux-3.13.6‘
内核的 allnoconfig 配置目标会把所有的内核选项都设置为no(除了一些必须设为yes的内核选项外),也就是把它们既不编译进内核,也不编译成模块。
# cd linux # make allnoconfig #把所有非必选的内核选项都设置为no
手动选择内核编译的配置
# make menuconfig
要手动勾选的内核选项 64-kit kernel #必须跟宿主机的平台保持一致 Ceneral setup --> Local version - append to kernel release #手动设定内核版本号 --> System V IPC #支持system V 风格的IPC(进程间通信),可选也可忽略。 Enable loadable module support --> Module unloading #选择支持动态卸载模块 Enable the block layer --> Block layer SG support v4 #选择支持使用块层 Processor type and features --> Symmetric multi-processing support #支持对称多处理器 --> Processor family --> Core 2/newer Xeon #选择合适的CPU类型 --> Multi-core scheduler suppor #支持多核调度 Bus options (PCI etc.) --> PCI support #选择支持PCI总线 Executable file formats / Emulations #可执行文件格式或类型 --> Kernel support for ELF binaries #支持ELF格式 --> Kernel support for scripts starting with #! #支持#!开头的脚本格式 Networking support --> Networking options --> TCP/IP networking #支持网络功能 --> Unix domain sockets #选择支持Unix domain sockets 协议(如果要在以下扩展nginx功能,这项必需) Device Drivers --> Generic Driver Options #选择支持把内核探测设备生成的设备文件挂载到/dev目录下 --> Maintain a devtmpfs filesystem to mount at /dev --> Automount devtmpfs at /dev, after the kernel mounted the rootfs --> SCSI device support --> SCSI device support --> SCSI disk support --> Fusion MPT device support --> Fusion MPT ScsiHost drivers for SPI --> Fusion MPT logging facility --> Network device support #选择网卡驱动 --> Ethernet driver support --> Intel devices --> Intel(R) PRO/1000 Gigabit Ethernet support --> Intel(R) PRO/1000 PCI-Express Gigabit Ethernet support --> Input device support #选择支持输入设备(键盘和鼠标) --> Mouse interface --> Keyboards --> Mice --> USB support #选择USB驱动 --> xHCI HCD (USB 3.0) support --> EHCI HCD (USB 2.0) support --> OHCI HCD (USB 1.1) support --> UHCI HCD (most Intel and VIA) support File systems --> The Extended 4 (ext4) filesystem #选择ext4类型文件系统
编译内核
# make -j 4
3、把宿主机上编译生成的bzImage复制到目标机上
# cp arch/x86_64/boot/bzImage /mnt/boot # sync #使得操作同步到磁盘
4、给目标机安装grub并提供grub配置文件
安装grub
# grub-install --root-directory=/mnt /dev/sdb # cd /mnt/boot # ls grub lost+found
给grub提供配置文件
[root@localhost boot]# cd grub/ [root@localhost grub]# vim grub.conf timeout=10 default=0 title Customed Linux( 3.13.6 ) root (hd0,0) kernel /bzImage ro root=/dev/sda2 init=/sbin/init
5、为目标机提供根文件系统
# cd /mnt/sysroot
# mkdir -pv bin sbin root home etc/init.d proc sys mnt media var tmp usr/{sbin,bin} lib646、在目标机sbin目录下提供init脚本
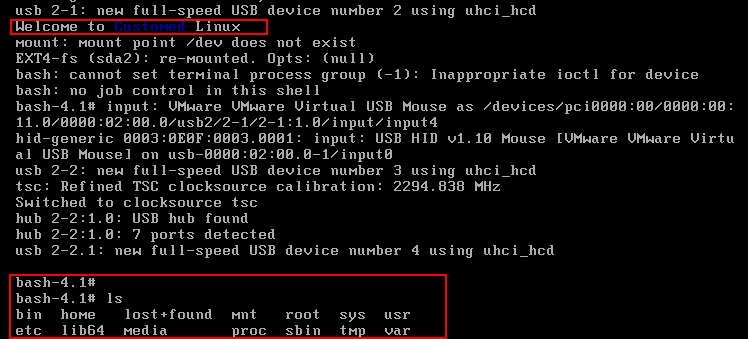
#!/bin/bash # echo -e "Welcome to \033[34mCustomed\033[0m Linux" mount -n -t proc proc /proc mount -n -t sysfs sysfs /sys mount -n -t devtmpfs none /dev mount -n -o remount,rw /dev/sdb2 / /bin/bash [root@localhost sbin]# chmod +x init #赋予该脚本执行权限 [root@localhost sbin]# ll init -rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 198 Aug 20 02:47 init [root@localhost sbin]# bash -n init #检查语法
7、使用bincp.sh脚本为目标机提供一些命令
[root@localhost ~]# ./bincp.sh Plz enter a command: mount Plz enter a command: umount Plz enter a command: ls Plz enter a command: ps Plz enter a command: kill Plz enter a command: cat Plz enter a command: bash [root@localhost ~]# sync #注意:操作完后一定要记得同步到磁盘上 [root@localhost ~]# chroot /mnt/sysroot #切换根目录来测试 bash-4.1# ls bin etc homelib64 lost+found media mnt proc root sbin sys tmp usrvar bash-4.1# exit exit [root@localhost ~]#
bincp.sh脚本内容如下:
#!/bin/bash
#
target=/mnt/sysroot/
[ -d $target ] || mkdir $target
preCommand() {
if which $1 &> /dev/null; then
commandPath=`which --skip-alias $1`
return 0
else
echo "No such command."
return 1
fi
}
commandCopy() {
commandDir=`dirname $1`
[ -d ${target}${commandDir} ] || mkdir -p ${target}${commandDir}
[ -f ${target}${commandPath} ] || cp $1 ${target}${commandDir}
}
libCopy() {
for lib in `ldd $1 | egrep -o "/[^[:space:]]+"`; do
libDir=`dirname $lib`
[ -d ${target}${libDir} ] || mkdir -p ${target}${libDir}
[ -f ${target}${lib} ] || cp $lib ${target}${libDir}
done
}
read -p "Plz enter a command: " command
until [ "$command" == ‘quit‘ ]; do
if preCommand $command ; then
commandCopy $commandPath
libCopy $commandPath
fi
read -p "Plz enter a command: " command
done8、启动目标机,进行初步测试
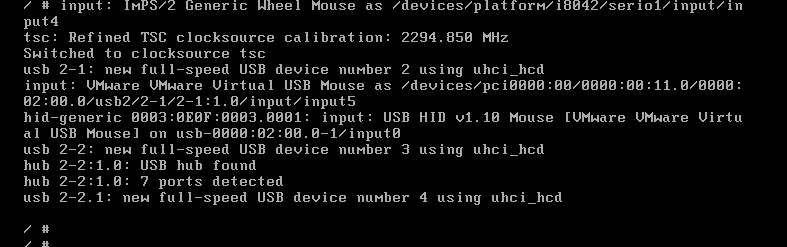
测试成功,在目标机上能正常打开bash命令行,相关的命令也有效
二、为目标机系统提供登录认证(使用busybox)
1、编译安装busybox
BusyBox介绍:
BusyBox 是一个集成了一百多个最常用linux命令和工具的软件。BusyBox 包含了一些简单的工具,例如ls、cat和echo等等,还包含了一些更大、更复杂的工具,例grep、find、mount以及telnet。有些人将 BusyBox 称为 Linux 工具里的瑞士***。简单的说BusyBox就好像是个大工具箱,它集成压缩了 Linux 的许多工具和命令,也包含了 Android 系统的自带的shell
其实,本质上就是给busybox程序创建软链接,就能根据其软链接名来调用对应软链接名的命令,如创建软链接ls -->busybox,就能使用软链接名ls来正常使用ls命令。
(1)安装依赖包
# yum install glibc-static
(2)下载、解压busybox-1.22.1.tar.bz2
# tar xf busybox-1.22.1.tar.bz2
(3)编译安装busybox-1.22.1
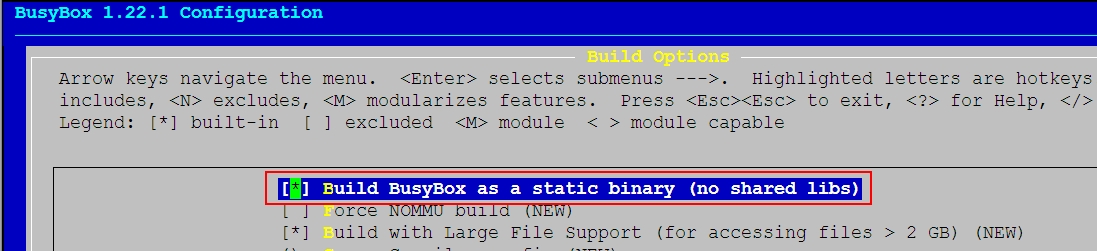
# cd busybox-1.22.1 # make menuconfig
选定为静态编译
(busybox没有bash,而是ash ,但是兼容bash)
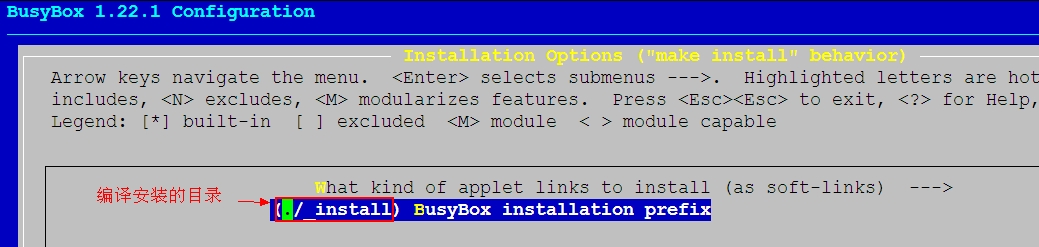
编译安装busybox
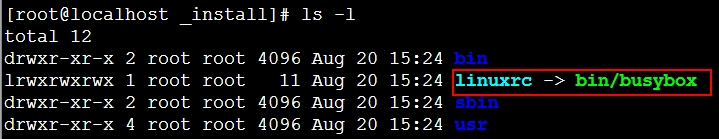
[root@localhost busybox-1.22.1]# make [root@localhost busybox-1.22.1]# make install [root@localhost busybox-1.22.1]# cd _install #默认安装在当前目录的_install目录下 [root@localhost _install]# ls bin linuxrc sbin usr
2、复制_install目录下的所有文件到目标机根目录下
[root@localhost sysroot]# ls bin etc homelib64 media mnt proc root sbin sys tmp usrvar [root@localhost sysroot]# rm * -rf #清空sysroot目录下的所有文件 [root@localhost _install]# cp -a * /mnt/sysroot [root@localhost sysroot]# ls bin linuxrc sbin usr [root@localhost sysroot]# rm linuxrc #linuxrc链接没用,可删除 rm: remove symbolic link `linuxrc‘? y
3、为目标机的sbin/init提供配置文件 /mnt/sysroot/etc/inittab
只提供物理控制台的inittab: [root@localhost sysroot]# vim etc/inittab ::sysinit:/etc/rc.d/rc.sysinit console::respawn:-/bin/sh (“-”表示该shell为 login shell。) ::ctrlaltdel:/sbin/reboot ::shutdown:/bin/umount -a -r
4、提供系统初始化脚本
[root@localhost rc.d]# vim rc.sysinit #在etc/rc.d/目录中提供系统初始化脚本 #!/bin/sh # echo -e "Welcome to \033[43mCustomed\033[0m Linux" echo "Remounting root filesystem" mount -n -o remount,rw /dev/sda2 / #以读写的方式重新挂载根文件系统 [root@localhost rc.d]# chmod +x rc.sysinit #给予该脚本执行权限
5、提供挂载文件fstab
[root@localhost sysroot]# vim etc/fstab #提供挂载文件fstab /dev/sda2 / ext4 defaults 0 0 /dev/sda1 /boot ext4 defaults 0 0 proc /proc proc defaults 0 0 sysfs /sys sysfs defaults 0 0
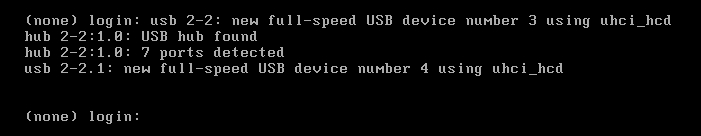
6、再次测试目标机系统是否能正常启动
7、进一步为目标机提供用户登录界面
为目标机提供用户登录界面的inittab
::sysinit:/etc/rc.d/rc.sysinit
::respawn:/sbin/getty 19200 tty1
::respawn:/sbin/getty 19200 tty2
::respawn:/sbin/getty 19200 tty3
::respawn:/sbin/getty 19200 tty4
::respawn:/sbin/getty 19200 tty5
::respawn:/sbin/getty 19200 tty6
::ctrlaltdel:/sbin/reboot
::shutdown:/bin/umount -a -r
测试:
(已有登录界面了)
8、为目标机提供用户和账号(能验证用户登录)
(1)使用openssl加密密码
[root@localhost sysroot]# openssl passwd -1 -salt `openssl rand -hex 4` Password: $1$f73e29d0$r.BamU/sKlQH9TmbT4j.e1
(2)提供/etc/passwd文件
root:x:0:0::/root:/bin/sh #busybox提供了sh,但没有提供bash hjq:x:500:500::/home/hjq:/bin/sh
(3)提供对应的/etc/shadow文件
root:$1$f73e29d0$r.BamU/sKlQH9TmbT4j.e1:16250:0:99999:7::: hjq:$1$f73e29d0$r.BamU/sKlQH9TmbT4j.e1:16250:0:99999:7::: [root@localhost etc]# chmod go= shadow #修改shadow文件的权限,只有管理员才有权限 [root@localhost etc]# ll shadow -rw------- 1 root root 117 Aug 20 18:27 shadow
(4)提供/etc/group文件
root:x:0: hjq:x:500
(5)为hjq用户创建家目录
[root@localhost sysroot]# mkdir /home/hjq
(6)提供命令行提示符
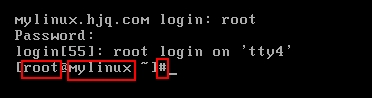
[root@localhost sysroot]# vim etc/profile export PS1=‘[\u@\h \W]\$‘ (注意:这里要用单引号,不能用双引号)
(7)提供主机名
[root@localhost sysroot]# mkdir etc/sysconfig [root@localhost sysroot]# vim etc/sysconfig/network HOSTNAME=www.hjq.com
(8)重新修改系统初始化脚本
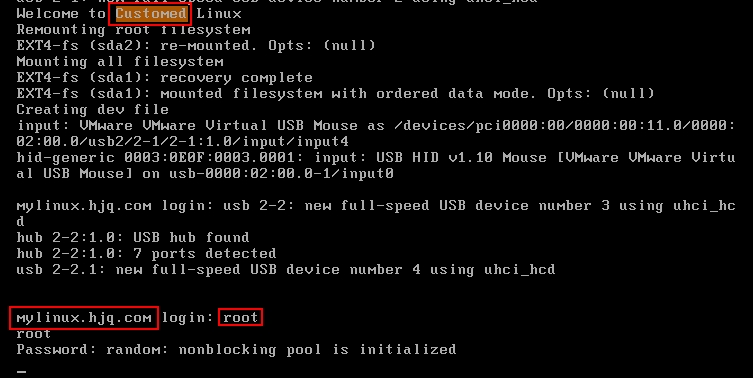
[root@localhost sysroot]# vim etc/rc.d/rc.sysinit #!/bin/sh echo -e "Welcome to \033[43mCustomed\033[0m Linux" echo "Remounting root filesystem" mount -n -o remount,rw /dev/sda2 / echo "Mounting all filesystem" mount -a #自动挂载/etc/fstab文件中定义的设备 echo "Creating dev file" mdev -s [ -f /etc/sysconfig/network ] && source /etc/sysconfig/network [ -z "$HOSTNAME" -o "$HOSTNAME" == "(none)" ] && hostname localhost || hostname $HOSTNAME [root@localhost etc]# sync
遇到的问题:在宿主机和目标机之间切换得太快了,在宿主机上修改的文件还没同步到目标机上,就会出现以下这种问题。
解决方法:
只有一个解决方法,重新格式化该硬盘
(1)备份/mnt/sysroot目录下的所有文件(使用cpio命令能尽可能保证文件的权限等信息不变)
[root@localhost sysroot]# find . | cpio -o -H newc | gzip -9 > /root/sysroot.gz 4387 blocks
(2)卸载/dev/sdb2
[root@localhost ~]# umount /mnt/sysroot umount: /mnt/sysroot: device is busy. (In some cases useful info about processes that use the device is found by lsof(8) or fuser(1)) [root@localhost ~]# fuser -km /mnt/sysroot #中止正在此挂载点的进程 /mnt/sysroot: 45955c 45985c 45998c 46036c 46270c 46375c 46466c 46522c 46558c 46587c 46620c [root@localhost ~]# umount /mnt/sysroot #成功卸载
(3)重新格式化
[root@localhost ~]# mke2fs -t ext4 /dev/sdb2
(4)重新挂载
[root@localhost ~]# mount /dev/sdb2 /mnt/sysroot [root@localhost ~]# cd /mnt/sysroot [root@localhost sysroot]# ls #重新格式化后,分区上的原有数据全被清除了 lost+found
(5)使用cpio命令重新恢复此前备份的文件
[root@localhost sysroot]# gunzip /root/sysroot.gz [root@localhost sysroot]# cpio -i < /root/sysroot 4387 blocks [root@localhost sysroot]# ls bin boot dev etc home lib64 lost+found media mnt proc root sbin sys tmp usr var
(6)测试
(能显示主机名,测试成功)
到此一个小型的Linux系统的基本功能已经基本实现的。
至于提供远程连接和nginx功能,由于篇幅不够,以后再补充!
本文出自 “恒则有成” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://hjqjk.blog.51cto.com/5970897/1544888
郑重声明:本站内容如果来自互联网及其他传播媒体,其版权均属原媒体及文章作者所有。转载目的在于传递更多信息及用于网络分享,并不代表本站赞同其观点和对其真实性负责,也不构成任何其他建议。