Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(一)--网络栈初始化
转载地址 http://blog.csdn.net/yming0221/article/details/7488828
作者:闫明
本文分析基于内核Linux Kernel 1.2.13
以后的系列博文将深入分析Linux内核的网络栈实现原理,这里看到曹桂平博士的分析后,也决定选择Linux内核1.2.13版本进行分析。
原因如下:
1.功能和网络栈层次已经非常清晰
2.该版本与其后续版本的衔接性较好
3.复杂度相对新的内核版本较小,复杂度低,更容易把握网络内核的实质
4.该内核版本比较系统资料可以查询
下面开始零基础分析Linux内核网络部分的初始化过程。
经过系统加电后执行的bootsect.S,setup.S,head.S,可以参考以前分析的0.11内核。原理相同。
进行前期的准备工作后,系统跳转到init/main.c下的start_kernel函数执行。
网络栈的层次结构如下图:(注:该图片摘自《Linux内核网络栈源代码情景分析》)
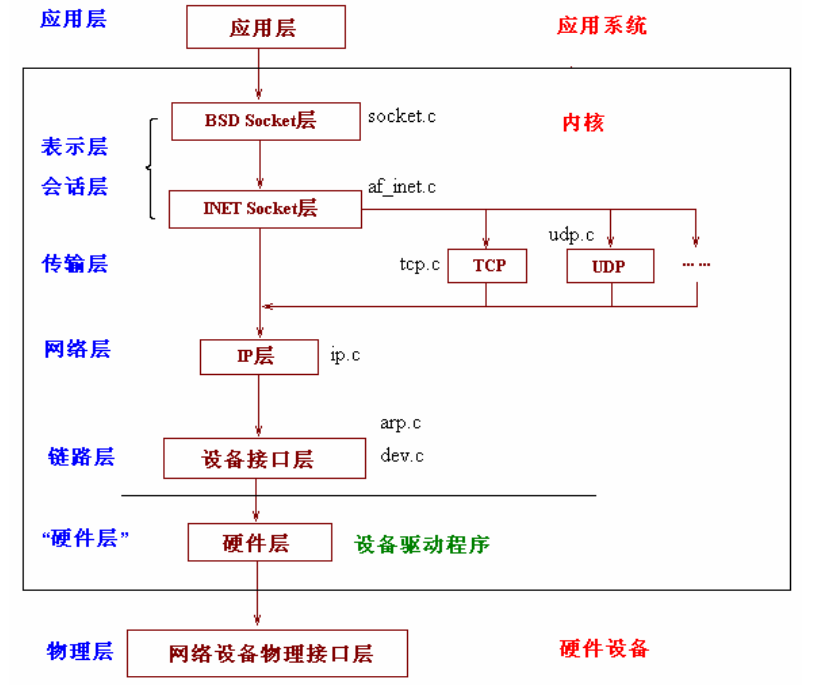
物理层主要提供各种连接的物理设备,如各种网卡,串口卡等;
链路层主要指的是提供对物理层进行访问的各种接口卡的驱动程序,如网卡驱动等;
网路层的作用是负责将网络数据包传输到正确的位置,最重要的网络层协议当然就是IP协议了,其实网络层还有其他的协议如ICMP,ARP,RARP等,只不过不像IP那样被多数人所熟悉;
传输层的作用主要是提供端到端,说白一点就是提供应用程序之间的通信,传输层最着名的协议非TCP与UDP协议末属了;
应用层,顾名思义,当然就是由应用程序提供的,用来对传输数据进行语义解释的“人机界面”层了,比如HTTP,SMTP,FTP等等,其实应用层还不是人们最终所看到的那一层,最上面的一层应该是“解释层”,负责将数据以各种不同的表项形式最终呈献到人们眼前。
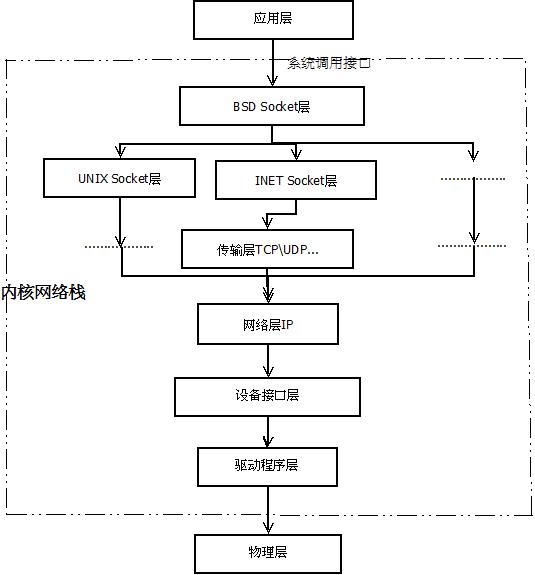
Linux网络协议栈结构
1,系统调用接口层,实质是一个面向用户空间应用程序的接口调用库,向用户空间应用程序提供使用网络服务的接口。
2,协议无关的接口层,就是SOCKET层,这一层的目的是屏蔽底层的不同协议(更准确的来说主要是TCP与UDP,当然还包括RAW
IP,
SCTP等),以便与系统调用层之间的接口可以简单,统一。简单的说,不管我们应用层使用什么协议,都要通过系统调用接口来建立一个SOCKET,这个SOCKET其实是一个巨大的sock结构,它和下面一层的网络协议层联系起来,屏蔽了不同的网络协议的不同,只吧数据部分呈献给应用层(通过系统调用接口来呈献)。
3,网络协议实现层,毫无疑问,这是整个协议栈的核心。这一层主要实现各种网络协议,最主要的当然是IP,ICMP,ARP,RARP,TCP,UDP等。这一层包含了很多设计的技巧与算法,相当的不错。
4,与具体设备无关的驱动接口层,这一层的目的主要是为了统一不同的接口卡的驱动程序与网络协议层的接口,它将各种不同的驱动程序的功能统一抽象为几个特殊的动作,如open,close,init等,这一层可以屏蔽底层不同的驱动程序。
5,驱动程序层,这一层的目的就很简单了,就是建立与硬件的接口层。
start_kernel函数经过平台初始化,内存初始化,陷阱初始化,中断初始化,进程调度初始化,缓冲区初始化等,然后执行socket_init(),最后开中断执行init()。
内核的网络战初始化函数socket_init()函数的实现在net/socket.c中
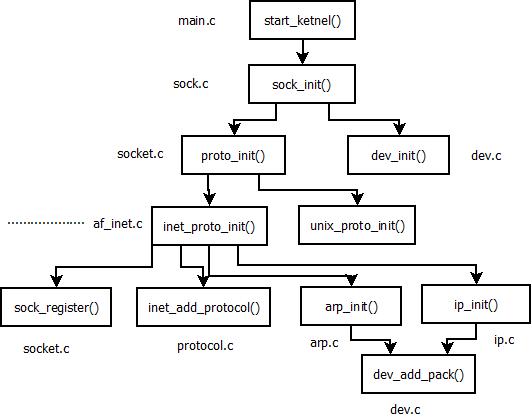
下面是该函数的实现
- void sock_init(void)//网络栈初始化
- {
- int i;
- printk("Swansea University Computer Society NET3.019\n");
- /*
- * Initialize all address (protocol) families.
- */
- for (i = 0; i < NPROTO; ++i) pops[i] = NULL;
- /*
- * Initialize the protocols module.
- */
- proto_init();
- #ifdef CONFIG_NET
- /*
- * Initialize the DEV module.
- */
- dev_init();
- /*
- * And the bottom half handler
- */
- bh_base[NET_BH].routine= net_bh;
- enable_bh(NET_BH);
- #endif
- }
其中的地址族协议初始化语句for (i = 0; i < NPROTO; ++i) pops[i] = NULL;
这里文件中定义的NPROTO为16
#define NPROTO16/* should be enough for now..*/
而pop[i]是如何定义的呢?
static struct proto_ops *pops[NPROTO];
proto_ops结构体是什么呢?该结构体的定义在include/linux/net.h中,该结构体是具体的操作函数集合,是联系BSD套接字和INET套接字的接口,可以把BSD套接字看做是INET套接字的抽象,结构示意图如下:
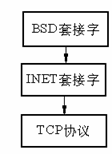
具体定义在net.h中
- struct proto_ops {
- int family;
- int (*create) (struct socket *sock, int protocol);
- int (*dup) (struct socket *newsock, struct socket *oldsock);
- int (*release) (struct socket *sock, struct socket *peer);
- int (*bind) (struct socket *sock, struct sockaddr *umyaddr,
- int sockaddr_len);
- int (*connect) (struct socket *sock, struct sockaddr *uservaddr,
- int sockaddr_len, int flags);
- int (*socketpair) (struct socket *sock1, struct socket *sock2);
- int (*accept) (struct socket *sock, struct socket *newsock,
- int flags);
- int (*getname) (struct socket *sock, struct sockaddr *uaddr,
- int *usockaddr_len, int peer);
- int (*read) (struct socket *sock, char *ubuf, int size,
- int nonblock);
- int (*write) (struct socket *sock, char *ubuf, int size,
- int nonblock);
- int (*select) (struct socket *sock, int sel_type,
- select_table *wait);
- int (*ioctl) (struct socket *sock, unsigned int cmd,
- unsigned long arg);
- int (*listen) (struct socket *sock, int len);
- int (*send) (struct socket *sock, void *buff, int len, int nonblock,
- unsigned flags);
- int (*recv) (struct socket *sock, void *buff, int len, int nonblock,
- unsigned flags);
- int (*sendto) (struct socket *sock, void *buff, int len, int nonblock,
- unsigned flags, struct sockaddr *, int addr_len);
- int (*recvfrom) (struct socket *sock, void *buff, int len, int nonblock,
- unsigned flags, struct sockaddr *, int *addr_len);
- int (*shutdown) (struct socket *sock, int flags);
- int (*setsockopt) (struct socket *sock, int level, int optname,
- char *optval, int optlen);
- int (*getsockopt) (struct socket *sock, int level, int optname,
- char *optval, int *optlen);
- int (*fcntl) (struct socket *sock, unsigned int cmd,
- unsigned long arg);
- };
可以看到,这里实际上就是一系列操作的函数,有点类似于文件系统中的file_operations。通过参数传递socket完成操作。
接下来是proto_init()协议初始化。
- void proto_init(void)
- {
- extern struct net_proto protocols[]; /* Network protocols 全局变量,定义在protocols.c中 */
- struct net_proto *pro;
- /* Kick all configured protocols. */
- pro = protocols;
- while (pro->name != NULL)
- {
- (*pro->init_func)(pro);
- pro++;
- }
- /* We‘re all done... */
- }
全局的protocols定义如下:
- struct net_proto protocols[] = {
- #ifdef CONFIG_UNIX
- { "UNIX", unix_proto_init },
- #endif
- #if defined(CONFIG_IPX)||defined(CONFIG_ATALK)
- { "802.2", p8022_proto_init },
- { "SNAP", snap_proto_init },
- #endif
- #ifdef CONFIG_AX25
- { "AX.25", ax25_proto_init },
- #endif
- #ifdef CONFIG_INET
- { "INET", inet_proto_init },
- #endif
- #ifdef CONFIG_IPX
- { "IPX", ipx_proto_init },
- #endif
- #ifdef CONFIG_ATALK
- { "DDP", atalk_proto_init },
- #endif
- { NULL, NULL }
- };
而结构体net_proto的定义net.h中为
- struct net_proto {
- char *name; /* Protocol name */
- void (*init_func)(struct net_proto *); /* Bootstrap */
- };
以后注重讨论标准的INET域
让我们回到proto_init()函数
接下来会执行inet_proto_init()函数,进行INET域协议的初始化。该函数的实现在net/inet/af_inet.c中
其中的
(void) sock_register(inet_proto_ops.family, &inet_proto_ops);
- int sock_register(int family, struct proto_ops *ops)
- {
- int i;
- cli();//关中断
- for(i = 0; i < NPROTO; i++) //查找一个可用的空闲表项
- {
- if (pops[i] != NULL)
- continue;//如果不空,则跳过
- pops[i] = ops;//进行赋值
- pops[i]->family = family;
- sti();//开中断
- return(i);//返回用于刚刚注册的协议向量号
- }
- sti();//出现异常,也要开中断
- return(-ENOMEM);
- }
参数中的inet_proto_ops定义如下:
- static struct proto_ops inet_proto_ops = {
- AF_INET,
- inet_create,
- inet_dup,
- inet_release,
- inet_bind,
- inet_connect,
- inet_socketpair,
- inet_accept,
- inet_getname,
- inet_read,
- inet_write,
- inet_select,
- inet_ioctl,
- inet_listen,
- inet_send,
- inet_recv,
- inet_sendto,
- inet_recvfrom,
- inet_shutdown,
- inet_setsockopt,
- inet_getsockopt,
- inet_fcntl,
- };
其中AF_INET宏定义为2,即INET协议族号为2,后面是函数指针,INET域的操作函数。
然后
- printk("IP Protocols: ");
- for(p = inet_protocol_base; p != NULL;) //将inet_protocol_base指向的一个inet_protocol结构体加入数组inet_protos中
- {
- struct inet_protocol *tmp = (struct inet_protocol *) p->next;
- inet_add_protocol(p);
- printk("%s%s",p->name,tmp?", ":"\n");
- p = tmp;
- }
- /*
- * Set the ARP module up
- */
- arp_init();//对地址解析层进行初始化
- /*
- * Set the IP module up
- */
- ip_init();//对IP层进行初始化
协议初始化完成后再执行dev_init()设备的初始化。
这是大体的一个初始化流程,讨论的不是很详细,后续会进行Linux内核网络栈源代码的详细分析。
郑重声明:本站内容如果来自互联网及其他传播媒体,其版权均属原媒体及文章作者所有。转载目的在于传递更多信息及用于网络分享,并不代表本站赞同其观点和对其真实性负责,也不构成任何其他建议。

































