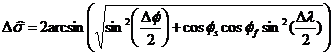HTML5编程之旅系列一:HTML5 Geolocation 初探
让我们假设这样一个场景,有一个web应用程序,它可以向用户提供附近不远处某商场的打折优惠信息。使用HTML5 Geolocation API(地理定位 API),可以请求用户共享他们的位置信息。
HTML5 Geolocation 技术应用的场景比较多,比如构建计算行走路程、GPS导航的社交应用等。
本文主要探讨 HTML5 Geolocation API,包括获取地理位置数据的途径,地理位置数据的隐私以及在实际中的应用等。
目前存在两种地理定位请求:单次定位请求和重复性的位置更新请求。
一、地理位置数据的获取
获取地理位置数据的方法有以下几种:
- IP地址地理定位:自动查找用户的IP地址,然后检索其注册的物理地址;
- GPS地理定位:通过收集运行在地球周围的多个GPS卫星信号来实现;
- Wi-Fi地理定位:通过三角距离计算得出(三角距离:用户当前位置到已知的多个Wi-Fi接入点的距离);
- 手机地理定位:通过用户到一些基站的三角距离确定;
- 用户自定义地理定位:用户自己输入地址、邮政编码和其他一些详细信息。
二、地理位置数据的隐私
HTML5 Geolocation 规范提供了一套保护用户隐私的机制,除非得到用户明确许可,否则不可能获取位置信息。
HTML5 地理定位浏览器和设备之间的交互如下所述:
- 用户从浏览器中打开位置感知应用程序;
- 应用程序Web页面加载,然后通过Geolocation函数调用请求位置坐标。浏览器拦截这一请求,然后请求用户授权。我们假设用户同意;
- 浏览器从其宿主设备中检索坐标信息。例如,IP地址、Wi-Fi 或 GPS 坐标。这是浏览器内部功能;
- 浏览器将坐标发送给受信任的外部定位服务,它返回一个详细位置信息,并将该位置信息发回给 HTML5 Geolocation 应用程序。
三、HTML5 Geolocation API介绍
在访问使用 HTML5 Geolocation API 的页面时,会触发隐私保护机制。但是如果仅仅是添加代码,而不被任何方法调用,则不会才触发隐私保护机制。
要使用 HTML5 Geolocation API,首先要检查浏览器是否支持,代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7 |
function
loadDemo(){If(navigator.geolocation){ document.getElementById("support").innerHTML = "HTML5 Geolocation supported.”}else{ ocument.getElementById("support”).innerHTML = "HTML5 Geolocation is not supported in
your browser.” }} |
单次定位请求API:
|
1
2
3 |
Void getCurrentPosition(in
PositionCallback successCallBack, in
optional PositionErrorCallBack errorCallback, in
optiona PositionOptions options) |
上述的函数要通过navigator.geolocation来调用,各个参数解释如下:
successCallBack:浏览器指明位置数据可用时调用的函数,即收到实际位置信息并进行处理的地方,此函数只接受一个参数:位置对象,包含坐标和一个时间戳;
errorCallback:在获取位置数据出错时的处理地方,向用户说明失败原因,可选参数,但是建议使用;
Options:此对象可调整 HML5 Geolocation服务的数据收集方式,可选;可以通过 JSON 对象进行传递,主要包括enableHighAccuracy(启用HML5 Geolocation服务的高精确度模式、timeout(当前位置所允许的最长时间)、maximumAge(浏览器重新计算位置的时间间隔)。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27 |
function
successCallBack(position){ var
latitude = position.coords.latitude; var
longitude = position.coords.longitude; var
accuracy = position.coords.accuracy; //此处可以添加代码,把上述三个值显示到页面中。 }ffunction errorCallback(error){ switch(error.code){ //UNKNOWN_ERROR = 0 需要通过message参数查找错误的更多信息 case
0: updateStatus("There was an error while retrieving your location:"
+ error.message); break; //PERMISSION_DENIED = 1 用户拒绝浏览器获得其共享位置 case
1: updateStatus("The user prevented this page form retrieving a location!"); break; //POSITION_UNAVAILABLE = 2 尝试获取用户位置,但失败 case
2: updateStatus("The browser was unable to determine your location:"
+ error.message); break; //TIMEOUT = 3 设置了可选的timeout值,尝试确定用户位置的过程超时 case
3: updateStatus("The browser timed out before retriveing the !"); break; }} |
重复性位置请求API:
|
1
2
3
4 |
var
watchId = navigator.geolocation.watchPosition(updateLocation,handleLocationError); //停止接收位置更新信息 navigator.geolocation.clearWatch(watchId); |
四、使用HML5 Geolocation构建应用
使用上述讲解的HML5 Geolocation API来实现 一个简单有用的Web应用程序—距离追踪器,以了解HML5 Geolocation 的强大之处。
本例主要讲述从网页被加载的地方到目前所在位置所经过的距离。使用众所周知的Haversine公式,其能够根据经纬度来计算地球上两点间的距离。如下:
关于上述原理,请参考网上其他教程。使用js实现的Haversine公式如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18 |
function
toRadians(degree){return
degree * Math.PI / 180 ;} function
distance(latitude1,longitude1,latitude1,longitude1){//R是地球的半径,以km为单位var
R = 6371;var
deltaLatitude = toRadians(latitude2 - latitude1);var
deltaLongitude = toRadians(longitude2 - longitude1); latitude1 = toRadians(latitude1);latitude2 = toRadians(latitude2); var
a = Math.sin(deltaLatitude / 2) * Math.sin(deltaLatitude / 2) + Math.cos(latitude1) * Math.cos(latitude2) * Math.sin(deltaLongitude / 2) * Math.sin(deltaLongitude / 2);var
c = 2 * Math.atan2(Math.sqrt(a),Math.sqrt(1-a));var
d = R * c;return
d;} |
HTML网页代码入下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127 |
<!DOCTYPE html><head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>HTML5 地理定位</title> <link rel="stylesheet"
href="styles.css"></head> <body onload="loadDemo()"> <h1>HTML5 地理位置追踪器</h1> <p id="status">你的浏览器不支持HTML5地理定位</p> <h2>当前位置:</h2><table border="1"><tr><th width="40"
scope="col"><h5>纬度</h5></th><td width="114"
id="latitude">?</td></tr><tr><td> 经度</td><td id="longitude">?</td></tr><tr><td>准确度</td><td id="accuracy">?</td></tr><tr><td>最近的时间戳</td><td id="timestamp">?</td></tr></table> <h4 id="currDist">当前旅行的距离: 0.0 km</h4><h4 id="totalDist">总的旅行距离: 0.0 km</h4> </body> <script text="text/javascript"> var
totalDistance = 0;var
lastLat;var
lastLong; Number.prototype.toRadians = function() {return
this * Math.PI / 180;} function
loadDemo(){If(navigator.geolocation){updateSatus("你的浏览器支持HTML5地理定位");navigator.geolocation.watchPosition(updateLocation,handleLocationError,{maximumAge:20000});}} function
updateSatus(message){document.getElementById("status").innerHTML = message;} function
distance(latitude1,longitude1,latitude1,longitude1){//R是地球的半径,以km为单位var
R = 6371;var
deltaLatitude = toRadians(latitude2 - latitude1);var
deltaLongitude = toRadians(longitude2 - longitude1); latitude1 = toRadians(latitude1);latitude2 = toRadians(latitude2); var
a = Math.sin(deltaLatitude / 2) * Math.sin(deltaLatitude / 2) + Math.cos(latitude1) * Math.cos(latitude2) * Math.sin(deltaLongitude / 2) * Math.sin(deltaLongitude / 2);var
c = 2 * Math.atan2(Math.sqrt(a),Math.sqrt(1-a));var
d = R * c;return
d;} function
updateLocation(position){var
latitude = position.coords.latitude; var
longitude = position.coords.longitude; var
accuracy = position.coords.accuracy; var
timestamp = position.timestamp;document.getElementById("latitude").innerHTML = latitude; document.getElementById("longitude").innerHTML = longitude; document.getElementById("accuracy").innerHTML = accuracy; document.getElementById("timestamp").innerHTML = timestamp; if(accuracy >= 500){updateStatus("不需要计算精确距离");return;} if((lastLat != null) && (lastLong !=null)){var
currentDistance = distace(latitude, longitude, lastLat, lastLong);document.getElementById("currDist").innerHTML = "当前旅行的距离: "
+ currentDistance.toFixed(4) + " km"; totalDistance += currentDistance; document.getElementById("totalDist").innerHTML = "总的旅行距离: "
+ currentDistance.toFixed(4) + " km";} lastLat = latitude;lastLong = longitude; updateStatus("成功更新位置。");} function
handleLocationError(error) { switch(error.code) { case
0: updateStatus("检索位置发生错误:"
+ error.message); break; case
1: updateStatus("用户阻止检索位置信息。"); break; case
2: updateStatus("浏览器不能检索位置信息:"
+ error.message); break; case
3: updateStatus("浏览器检索位置信息超时。"); break; } } </script> </html> |
本文链接:《HTML5编程之旅》第1站——HTML5 Geolocation 初探
via oschina
郑重声明:本站内容如果来自互联网及其他传播媒体,其版权均属原媒体及文章作者所有。转载目的在于传递更多信息及用于网络分享,并不代表本站赞同其观点和对其真实性负责,也不构成任何其他建议。